Mobile Security in Preventing Information Leak with Scene Detection and Document Image Analysis
An APP to analyze document images and recognize scenes running on the edge without cloud support
Abstract
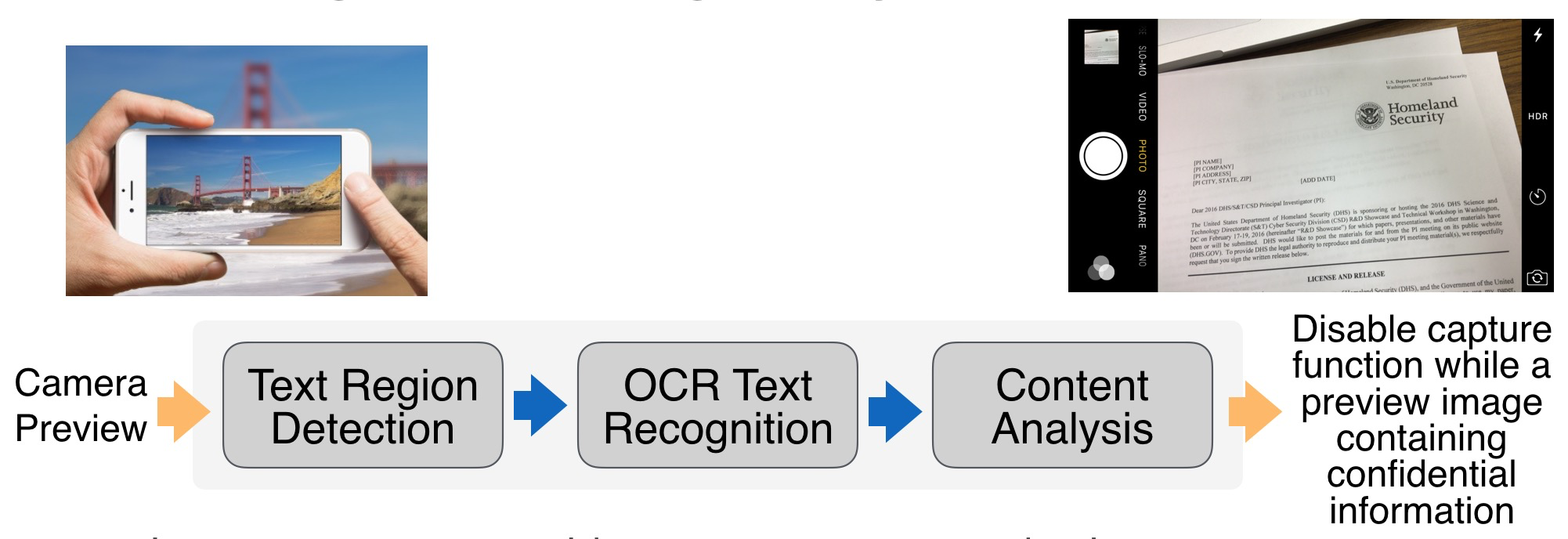
How to prevent information leak from mobile devices is a big challenge for corporates and governments. Especially, cameras on smartphones are pervasive and confidential information could be easily captured by just one click. Here, we design an APP running in the background for document image analysis, logo detection, and scene recognition, which is running on the edge without cloud support with frame rate 10 fps (on iPhone 7). Once detecting any confidential documents or secured scene on the preview, the APP will send out warnings to the corporates/governments and disable the smartphone immediately. For more details, please see demo videos.
Paper Download
We proposed the method to shrink network architectures of deep learning models, while keeping the detection accuracy. The method was published in CVPR2018 as a spotlight paper.
Ruichi Yu, Ang Li, Chun-Fu Chen, Jui-Hsin(Larry) Lai , Vlad I. Morariu, Xintong Han, Mingfei Gao, Ching-Yung Lin, and Larry S. Davis, “ NISP: Pruning Networks using Neuron Importance Score Propagation ”, in Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition(CVPR), 2018Patents
Method, system and computer program product configured to protect documents to be captured in camera preview
Abstract
A method includes analyzing a preview image made by an image sensor when operating in a preview image mode to determine if the preview image contains some portion that corresponds to information that is considered not subject to being imaged. The method further includes, if it is determined that the preview image does comprise some image portion that corresponds to information that is considered not subject to being imaged, disabling the image sensor from capturing an image that would correspond to the preview image. Analyzing can include accessing a data storage that contains representations of information that is considered not subject to being imaged for comparison with image features extracted from the preview image, where the data storage is at least one of contained in a device that also contains the image sensor, or is located remotely from the device and can be accessed via a wireless connection.
Pruning Redundant Neurons and Kernels of Deep Convolutional Neural Networks
Abstract
Method and apparatus for optimizing a convolutional neural network (CNN). A respective measure of importance is calculated for each of a plurality of elements within a CNN. A first one of the measures of importance is calculated by back propagating a second one of the measures of importance through the CNN. One or more of the plurality of elements is pruned from the CNN, based on the calculated measures of importance.
Method, system and computer program product for selective image capture
Abstract
A method includes analyzing a preview image made by an image sensor when operating in a preview image mode to determine if the preview image contains some portion that corresponds to information that is considered not subject to being imaged. The method further includes, if it is determined that the preview image does comprise some image portion that corresponds to information that is considered not subject to being imaged, disabling the image sensor from capturing an image that would correspond to the preview image. Analyzing can include accessing a data storage that contains representations of information that is considered not subject to being imaged for comparison with image features extracted from the preview image, where the data storage is at least one of contained in a device that also contains the image sensor, or is located remotely from the device and can be accessed via a wireless connection.
Identity recognition with living signatures from multiple devices
Abstract
Identity recognition is achieved using user's living signatures, such as a heartbeat signal, from multiple devices. A user requests identity recognition for using a first registered device, such as a mobile device. The request is provided to a cloud. When the cloud confirms the mobile device is a registered device, the cloud directs the first registered device to upload the user living signature to the cloud. The cloud also sends a request to a user second registered device to upload the user living signature from the second registered device to the cloud. The user second registered device may be a headband monitor, watch, Google glasses, or the like capable of monitoring and uploading the user living signature to the cloud. The cloud compares both living signature signals from the first registered device and from the second registered device. If the signals are matched, the user identity is confirmed. If the signals are not matched, the user identity is not confirmed. Preferably the first registered device is a mobile device.
Demo Video - Document Image Analysis
Real-time document image analysis.
If you cannot see the video below, click the link https://www.youtube.com/embed/eH_wsJYbgZ8
Demo Video -- Scene Recognition
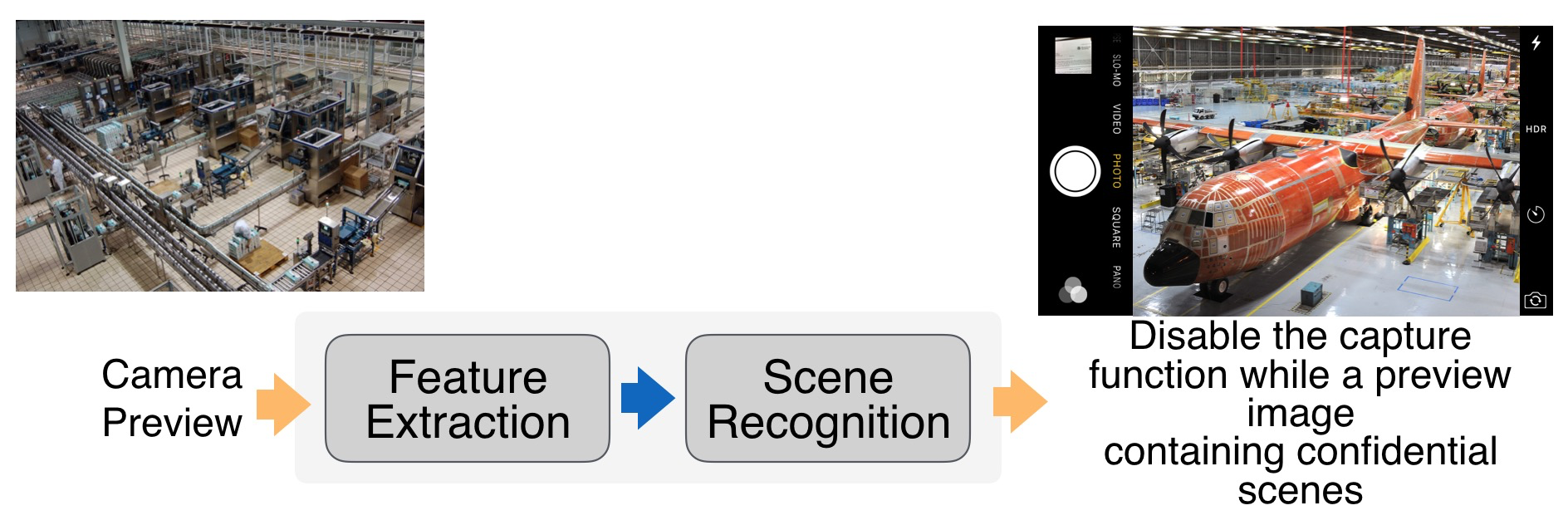
Running CNN models for scene recognition
If you cannot see the video below, click the link https://www.youtube.com/embed/7oCsQeqL9a8
Running Food-101 models for Food Recognition
If you cannot see the video below, click the link https://www.youtube.com/embed/tSFic565HlM